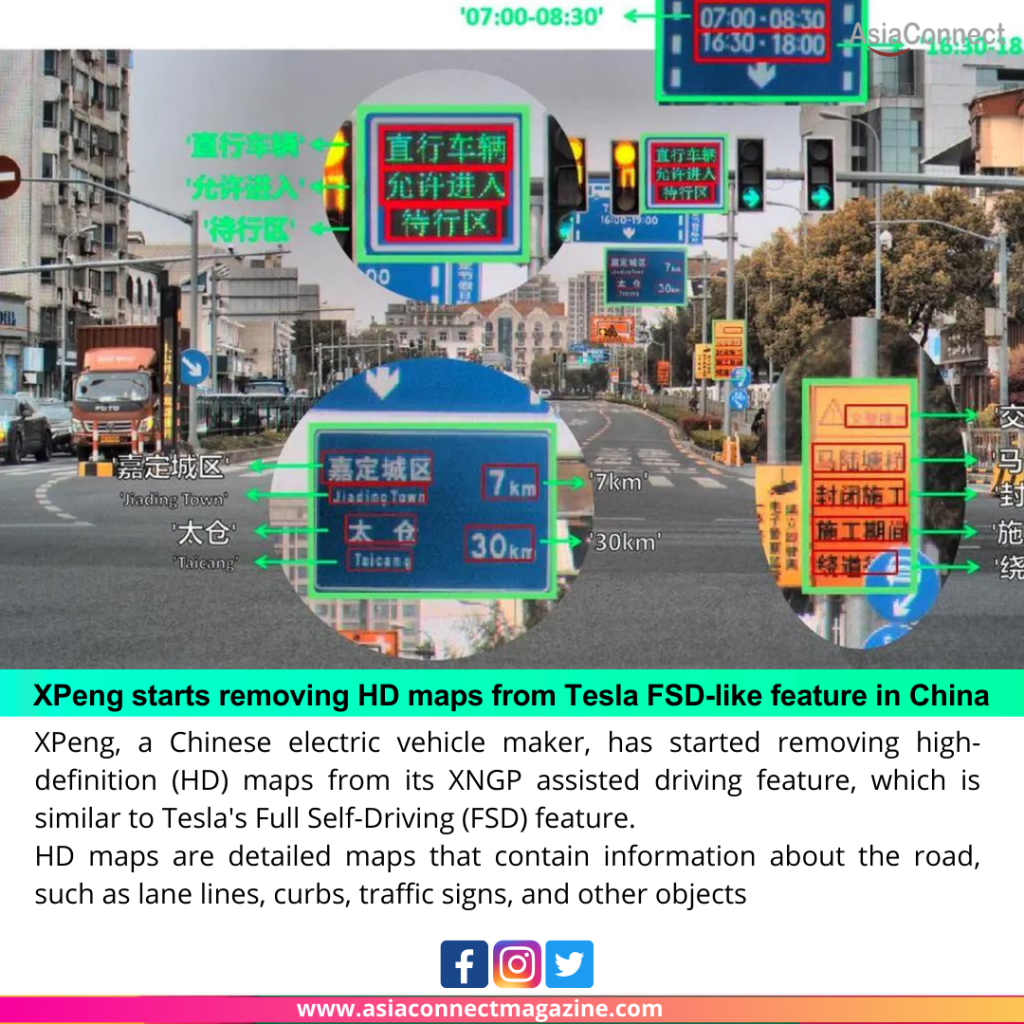
XPeng, a Chinese electric vehicle maker, has started removing high-definition (HD) maps from its XNGP assisted driving feature, which is similar to Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) feature.
HD maps are detailed maps that contain information about the road, such as lane lines, curbs, traffic signs, and other objects. These maps are used by assisted driving systems to help them navigate the road safely.
XPeng says that it is removing HD maps from XNGP because it believes that it can achieve a higher level of autonomous driving without them. The company is using a combination of cameras, radars, and other sensors to create its own real-time map of the road.
XPeng’s decision to remove HD maps is significant because it is the first major automaker to do so. Tesla has been using HD maps in its FSD system since 2016.
There are a few reasons why XPeng may be removing HD maps from XNGP. First, HD maps are expensive to create and maintain. Second, HD maps can be inaccurate, especially in areas where the road is constantly changing. Third, XPeng may believe that it can achieve a higher level of autonomous driving without HD maps by using its own real-time map of the road.
There are also some potential risks associated with removing HD maps from assisted driving systems. Without HD maps, assisted driving systems may have difficulty navigating complex road situations, such as intersections and construction zones. Additionally, assisted driving systems without HD maps may be more likely to make mistakes, such as changing lanes into oncoming traffic or failing to stop at red lights.
XPeng says that it is aware of these risks and is taking steps to mitigate them. The company is testing XNGP in a variety of road conditions and is developing new algorithms to help the system navigate complex road situations. Additionally, XPeng is working with Chinese regulators to develop safety standards for assisted driving systems without HD maps.
It is too early to say whether XPeng’s decision to remove HD maps from XNGP will be successful. However, the company’s move is a sign that the auto industry is moving towards a future where assisted driving systems will not rely on HD maps.
Here are some of the potential benefits of removing HD maps from assisted driving systems:
- Reduced costs: HD maps can be expensive to create and maintain. Removing HD maps from assisted driving systems can help to reduce costs for both automakers and consumers.
- Increased accuracy: HD maps can be inaccurate, especially in areas where the road is constantly changing. Removing HD maps from assisted driving systems can help to improve the accuracy of these systems.
- Improved performance: XPeng believes that it can achieve a higher level of autonomous driving without HD maps by using its own real-time map of the road. This could lead to improved performance for assisted driving systems in terms of safety, efficiency, and comfort.
Here are some of the potential risks of removing HD maps from assisted driving systems:
- Difficulty navigating complex road situations: Without HD maps, assisted driving systems may have difficulty navigating complex road situations, such as intersections and construction zones.
- Increased likelihood of mistakes: Assisted driving systems without HD maps may be more likely to make mistakes, such as changing lanes into oncoming traffic or failing to stop at red lights.
- Regulatory challenges: Regulators in some countries may be hesitant to approve assisted driving systems without HD maps.
Overall, the removal of HD maps from assisted driving systems is a complex issue with both potential benefits and risks. It remains to be seen whether the benefits will outweigh the risks. However, XPeng’s decision to remove HD maps from XNGP is a significant development that could have a major impact on the future of the auto industry.




